Domain and Range
Domain
The domain of a function is the set of values of the independent variable (x) for which the function is defined.
There are two common mathematical operations that are undefined: square root of a negative number and division by zero.
Because a square root cannot successfully act on a negative number, the domain of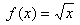 is all real numbers x such that
is all real numbers x such that 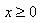 . In set notation, this would be written
. In set notation, this would be written 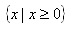 .
.
Division by zero is undefined; therefore values for x that produce a zero denominator are excluded from the domain. For instance, the function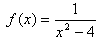 has a domain of all real numbers except
has a domain of all real numbers except 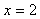 and
and 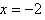 . In set notation, this would be written
. In set notation, this would be written 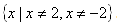 .
.
There are two common mathematical operations that are undefined: square root of a negative number and division by zero.
Because a square root cannot successfully act on a negative number, the domain of
Division by zero is undefined; therefore values for x that produce a zero denominator are excluded from the domain. For instance, the function