Graphing Overview
Graphing Families Overview
Absolute Value Functions
Absolute value is defined as a number’s distance from zero. Since distance is always positive or zero, absolute value functions will always produce positive or zero outputs.
Absolute value functions have equations in the form: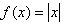 . The graph has reflectional symmetry across a vertical line through the vertex. Absolute value functions can be piece-wise defined as two linear functions with different domains.
. The graph has reflectional symmetry across a vertical line through the vertex. Absolute value functions can be piece-wise defined as two linear functions with different domains.
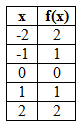
See the table and graph of a basic absolute value function below.
Absolute value functions have equations in the form:
See the table and graph of a basic absolute value function below.
 |

|
Here are some situations that can be modeled by absolute value functions:
- Distances in real life (time vs. distance).
- Exchanging currency (old currency vs. new).