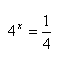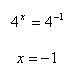Logarithms
| Site: | Clare-Gladwin RESD |
| Course: | Michigan Algebra II KHauck |
| Book: | Logarithms |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Thursday, January 29, 2026, 2:09 AM |
Description
Method 1
There are many different types of logarithmic equations. The first type uses properties to convert more than one log into a single log expression and then applies inverses to solve.
Example 1 Solve log3 4 + log3 x = 1
Step 1. Use properties to convert to a single log.
Step 2. Translate the log equation to its equivalent exponential form.
Step 3. Solve for x.
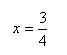
Example 2
![]()
Step 2. Translate the log equation to its equivalent exponential form.
Step 3. If needed, change the two expressions to the same base and solve for x.
Method 2
Another type of log equation is one where there is a log on both sides of the equal sign. To solve this type of equation, use the inverse relationship between logs and exponents.
Example 1 Solve the equation ![]()
Step 1. Use Product of a Power Property to convert to a single log.
![]()
Step 2. Use the inverse operation of exponents on both sides of the equals sign. Since the log has a base of 2, use an exponential base of 2.
![]()
Step 3. Since logs and exponents are inverses, the exponent base and the log base cancel.
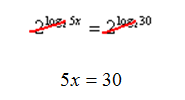
Step 4 . Solve for x.
![]()
Example 2
Solve the equation ![]()
Step 1. Use Power of a Power Property to convert to a single log.
![]()
Step 2. Use the inverse operation of exponents on both sides of the equals sign. Since the common log has a base of 10, use an exponential base of 10.
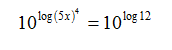
Step 3. Since logs and exponents are inverses, the exponent base and the log base cancel.
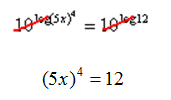
Step 4 . Solve for x.
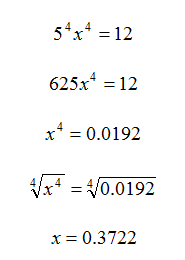
Video Lesson
To learn how to solve log equations, select the following link:Guided Practice
To solidify your understanding of evaluating exponential and logarithmic equations, visit the following link to Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Homework Help Online. It provides examples, video tutorials, and interactive practice with answers available. The Practice and Problem Solving section has two parts. The first part offers practice with a complete video explanation for the type of problem with just a click of the video icon. The second part offers practice with the solution for each problem only a click of the light bulb away.
Practice
*Note: If Google Docs displays, “Sorry, we were unable to retrieve the document for viewing,†refresh your browser.
Answer Key
*Note: If Google Docs displays, “Sorry, we were unable to retrieve the document for viewing,†refresh your browser.
Sources
Sources used in this book:Embracing Mathematics, Assessment & Technology in High Schools; a Michigan Mathematics & Science Partnership Grant Project
Glencoe, McGraw-Hill, "Properties of Logs." http://www.glencoe.com/sec/math/studytools/cgi-bin/msgQuiz.php4?isbn=0-07-827999-2&chapter=10&lesson=3&headerFile=4&state=fl (accessed 7/13/2010).
Holt, Rinehart & Winston, "Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations." http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/homework_help/alg2/alg2_ch07_05_homeworkhelp.html (accessed 7/13/2010).
Holt, Rinehart & Winston, "Solving Logarithmic Equations." http://my.hrw.com/math06_07/nsmedia/lesson_videos/alg2/player.html?contentSrc=7152/7152.xml (accessed 7/13/2010).