Overview
| Site: | Clare-Gladwin RESD |
| Course: | Michigan Algebra II KHauck |
| Book: | Overview |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, February 24, 2026, 10:16 PM |
Description
Overview
Overview
Recall from Algebra I that a function models a process or algorithm for turning inputs into outputs. The traditional image of a function is a machine, with a slot on one side where numbers go in and a slot on the other side where numbers come out.
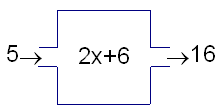
Figure 1: This function turns 5 into 16.
This image demonstrates that the function is the process, not the numbers alone.
Objectives
The purpose of this unit is to become familiar with functions and function notation. You will learn to add, subtract, multiply and divide functions. You will identify the different families of functions, create equations of their transformations and determine their domain and range. You will also perform composition of functions and relate this process to an understanding of inverse functions.
Â
Expectations
MI Alg2 High School Content Expectations
Addressed Within the Families of Functions Unit
L1.2.1 Use mathematical symbols to represent quantitative relationships and situations.
A1.1.1 Give a verbal description of an expression that is presented in symbolic form, write an algebraic expression from a verbal description, and evaluate expressions given values of the variables.
A1.2.8 Solve an equation involving several variables (with numerical or letter coefficients) for a designated variable, and justify steps in the solution.
A2.1.1 Determine whether a relationship (given in contextual, symbolic, tabular, or graphical form) is a function, and identify its domain and range.
A2.1.2 Read, interpret, and use function notation, and evaluate a function at a value in its domain.
A2.1.3 Represent functions in symbols, graphs, tables, diagrams, or words, and translate among representations.
A2.1.7 Identify and interpret the key features of a function from its graph or its formula(s).
A2.2.1 Combine functions by addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
A2.2.2 Apply given transformations to parent functions, and represent symbolically.
A2.2.3 Recognize whether a function (given in tabular or graphical form) has an inverse, and recognize simple inverse pairs.
A2.3.1 Identify a function as a member of a family of functions based on its symbolic or graphical representations; recognize that different families of functions have different asymptotic behavior.
A2.3.3 Write the general symbolic forms that characterize each family of functions.
A2.4.1 Identify the family of functions best suited for modeling a given real-world situation.
Sources
Sources used in this book:Embracing Mathematics, Assessment & Technology in High Schools; a Michigan Mathematics & Science Partnership Grant Project
Kenny Felder, "Function Concepts -- What is a Function?," Connexions, December 30, 2008, http://cnx.org/content/m18189/1.2/
Kenny Felder, "Function Concepts -- Function Notation," Connexions, April 15, 2009, http://cnx.org/content/m18188/1.3/