Factored Form
| Site: | Clare-Gladwin RESD |
| Course: | Michigan Algebra I |
| Book: | Factored Form |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, January 2, 2026, 2:01 PM |
Description
Factored Form
Quadratic Equations
When a quadratic function crosses the x-axis, those x-values are called the roots or zeros of the function. For a quadratic function that has real roots,|
For example: See how the graph of |
|
The factored form of a quadratic equation also tells you where the x-intercepts are located. The x-intercepts of the equation are the x-values that will make y = 0.
Graphing
To graph a quadratic equation in factored form, first identify the x-intercepts. Use the a-value to determine if the graph will open up or down. The vertex of the parabola can be found exactly midway between the two x-intercepts, using the symmetry of the parabola. It is then possible to find the y-intercept by substituting x = 0 into the equation and solving. Finally, use the symmetry of the graph to find a point on the other side of the axis of symmetry.Example
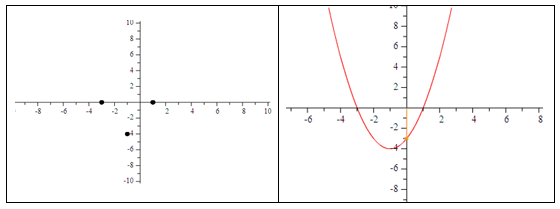
Make a graph of the following function: f(x) = (x + 3) (x - 1)Step 1. Determine the x-intercepts.
0 = (x + 3)(x - 1)
x + 3 = 0 or x - 1 = 0
x = -3 or x = 1
Step 2. Find the a-value.
The a-value is positive one, so the graph opens up.
Step 3. Calculate the vertex of the graph.
The midpoint of the x-intercepts is: ![]() .
.
The y-coordinate is ![]()
The vertex is (-1, -4).
Example Continued
The y-intercept is ![]()
The y-intercept is (0, -3).
The symmetry point is (-2, -3).
Step 5. Plot the points and sketch the curve.
Interactive Activity
To see how quadratic graphs change as factors change, select the following link:Factored Form Graphing
Practice
Factored Form Graphing WorksheetAnswer Key
Factored Form Graphing Answer KeyWriting Equations
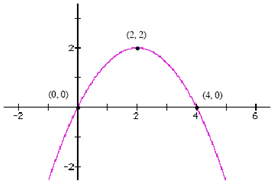
The x-intercepts of the graph are (0, 0) and (4, 0).
Step 2. Substitute the x-intercepts into the general form.
![]()
Step 3. Substitute another point from the graph into the general form and solve for the a-value.
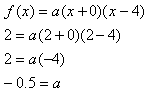
Step 4. Substitute the a-value into the formula.
![]()
Practice
Writing Factored Form Equations WorksheetAnswer Key
Writing Factored Form Equations Answer KeySources
Embracing Mathematics, Assessment & Technology in High Schools; A Michigan Mathematics & Science Partnership Grant Project
Hot Math, "Factored Form Applet." http://hotmath.com/util/hm_flash_movie. html?movie=/learning_activities/interactivities/quadratics.swf&title=Quadratics%20in%20Factored%20Form (accessed 08/05/2010).
"What the Factored Form Can Tell You About a Graph." http://algebra-tutoring.com/solving-quadratic-equations-6.htm (accessed 8/05/2010).
